

By Lynne Vosper
In commemoration of the 80th anniversary of the D-Day Landings at Normandy, we would like to share some of the iconic images that portray the important part played by Falmouth, the Fal, and the Helford during the preparations for the invasion on 6 June 1944 when 150,000 troops and over 5,000 ships and landing craft took part in the largest amphibious invasion in history.
Together with the associated airborne operations and naval and aerial bombardment, it marked the beginning of the liberation of France and western Europe.
Commander Kenneth Edwards RN, in a quotation from his book ‘Operation Neptune’ stated “The invasion of Hitler’s “European Fortress” which laid the firm foundation of victory, was known by the code name of “Operation Overlord”. “Neptune” was the code name for the naval component of “Overlord”, which His Majesty King George VI described as “The greatest combined operation the world has ever seen – perhaps the greatest it will ever see”. Success in “Neptune” was the first essential to success in “Overlord” and to victory.
‘D’ stands for ‘Day’, meaning it is short for ‘Day-Day’. Before the allied attack in June 1944 there would have been many D-Days, however it was so iconic that it came to be used solely when referring to the beginning of Operation Overlord.
America joined the war following the attack on the American naval base of Pearl Harbor in the Hawaiian Islands on Sunday 7 December 1941 by Japanese planes. A few weeks after this event 4,000 Americans had arrived in Britain and 16 months after that time over one and half million American troops were stationed in Britain preparing for the Allied invasion of the coast of Normandy.
The 29th Infantry Division, the Blue and Grey, arrived at Greenock, Scotland in October 1942 (19,000 troops). After spending months training on Salisbury Plain and in Dorset they moved to be stationed in Devon and Cornwall. American soldiers, sailors and airmen were stationed all along the south west coast. It was said that Cornwall was almost the “49th State of the Union” as US troops filled the county in late 1943 and early 1944.
A programme of providing accommodation, known as ‘Bolero’, created thousands of temporary camps throughout England’s southern counties, taking over cliffs, woods, fields, houses, hotels, villages and towns to house the members of the US forces. Some troops were housed in tents forming camps along the sides of the roads and were known as ‘sausage camps’.
In preparation for the D-Day invasion of the beaches of Normandy, the US Navy established an Advanced Amphibious Base in the fields to the west of the Beacon in Falmouth in the summer of 1943. The main entrance was at the end of Tregothnan Road, and the camp went beside the main road into Falmouth at Dracaena Avenue and up over the Beacon. The camp consisted of Nissen huts and larger Quonset huts. At this time there were 3,000 US Navy personnel based at Falmouth.
The entrance to the US Navy Advanced Amphibious Base on the Beacon, Falmouth
(‘Falmouth in Old Photographs’ by Peter Gilson)
The camp in Falmouth went along Dracaena Avenue and up over the Beacon
with the entrance at the end of Tregothnan Road.
(‘Falmouth’s Wartime Memories as told to Trelawney’)
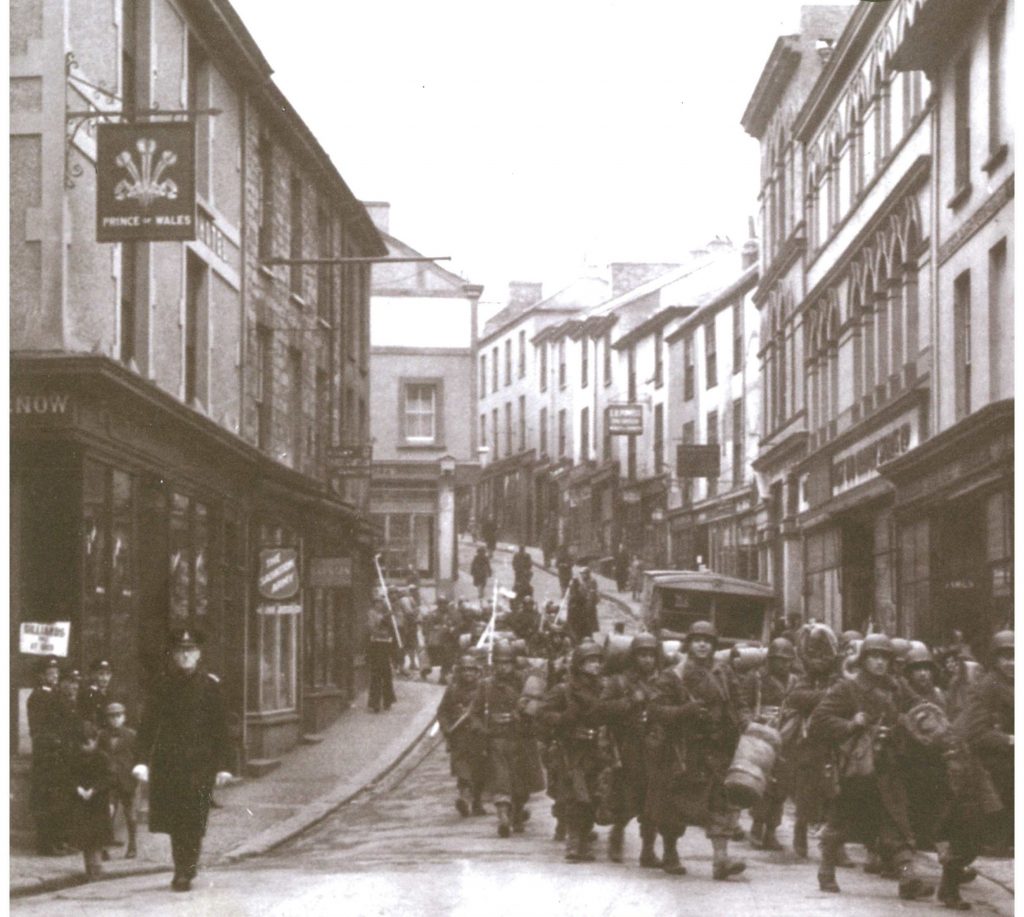

US Troops march along Falmouth’s Webber Street and Market Strand to embark at Prince of Wales Pier
for Operation Duck 1 on 30 December 1943, one of the many dress rehearsals for D-Day.
(Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society)

US Troops preparing to embark at Prince of Wales Pier for
Operation Duck 1 in December 1943, one of the dress rehearsals for D-Day.
(Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society)
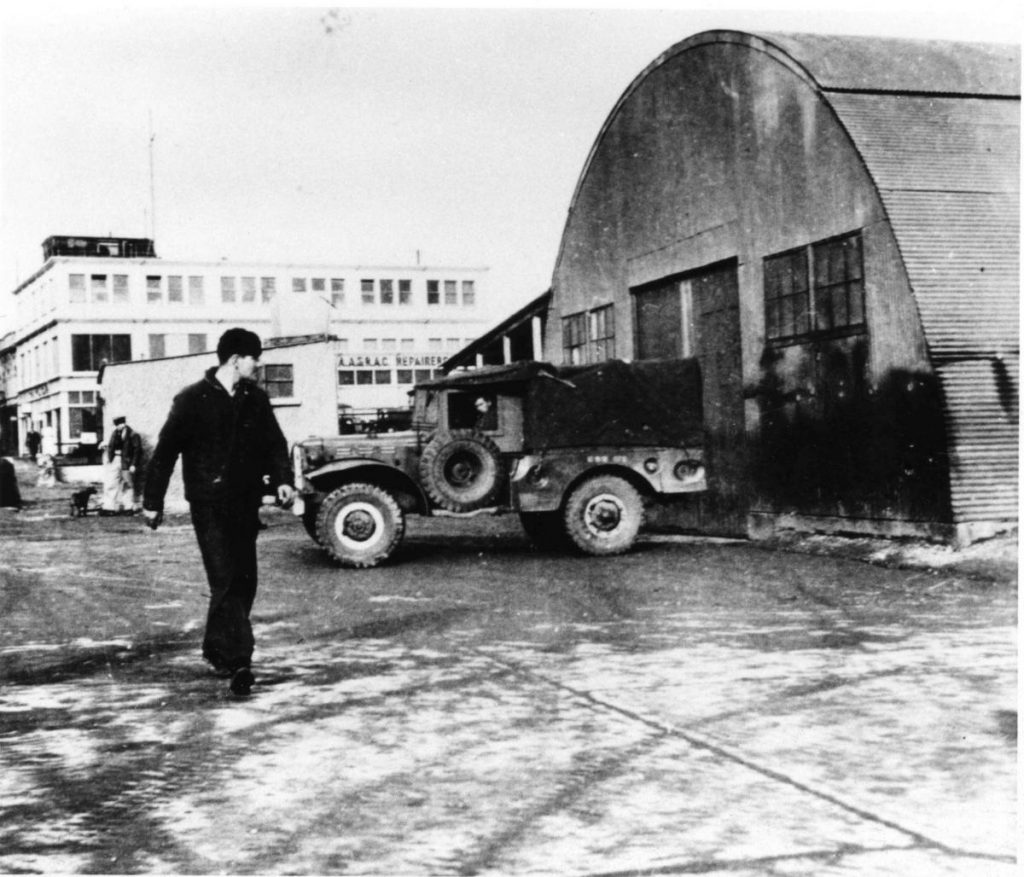

Grove Place, Falmouth was taken over by the naval maintenance teams as workshops.
(Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society)
Strategically located Falmouth, with its dry docks and ship repair facilities, was engaged in vital war work, much of it secret. Grove Place and Harvey’s Yard in Falmouth, and three other sites nearby, were chosen for loading heavy vehicles in West Cornwall – one on the north side of the Helford River at Polgwidden Cove (Trebah Beach) and two on the Fal at Tolverne and Turnaware Point. These embarkation points had to be prepared with roads and piers being built and flexible concrete matting laid to form “hards”, and their locations were closely guarded.
The hards in the Falmouth and Helford area had the following identifying codes:
The Prince of Wales Pier, Falmouth and Messack Point at St Just-in-Roseland were also used to embark troops onto Landing Ships Infantry (large), (LSI(L)s).
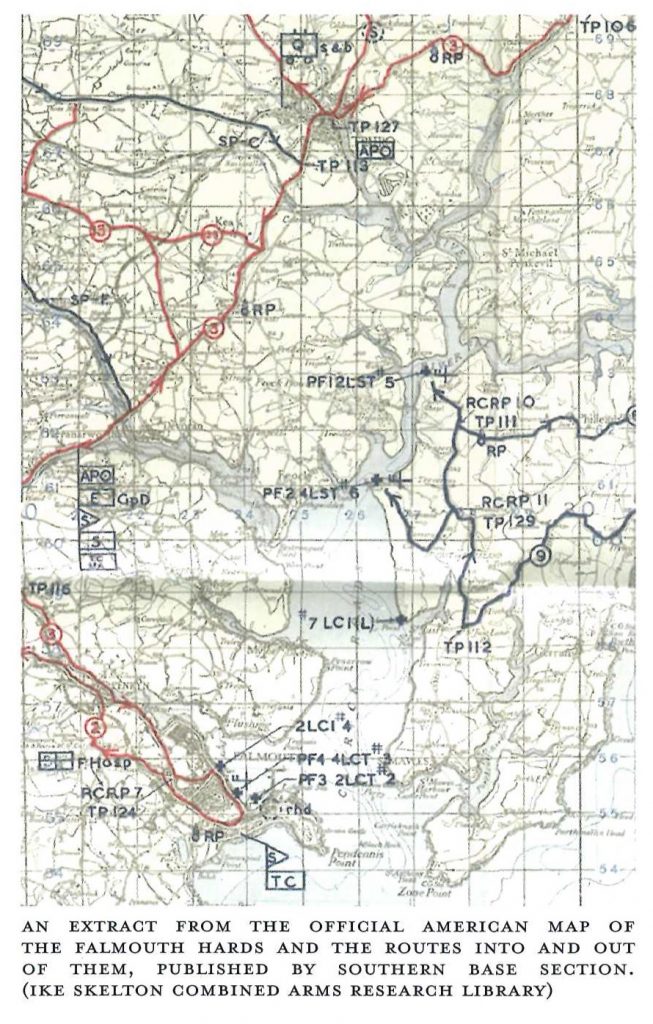
Image from ‘D-Day, Operation Overlord, Cornwall and Preparation for the D-Day landings
By Roderick De Normann
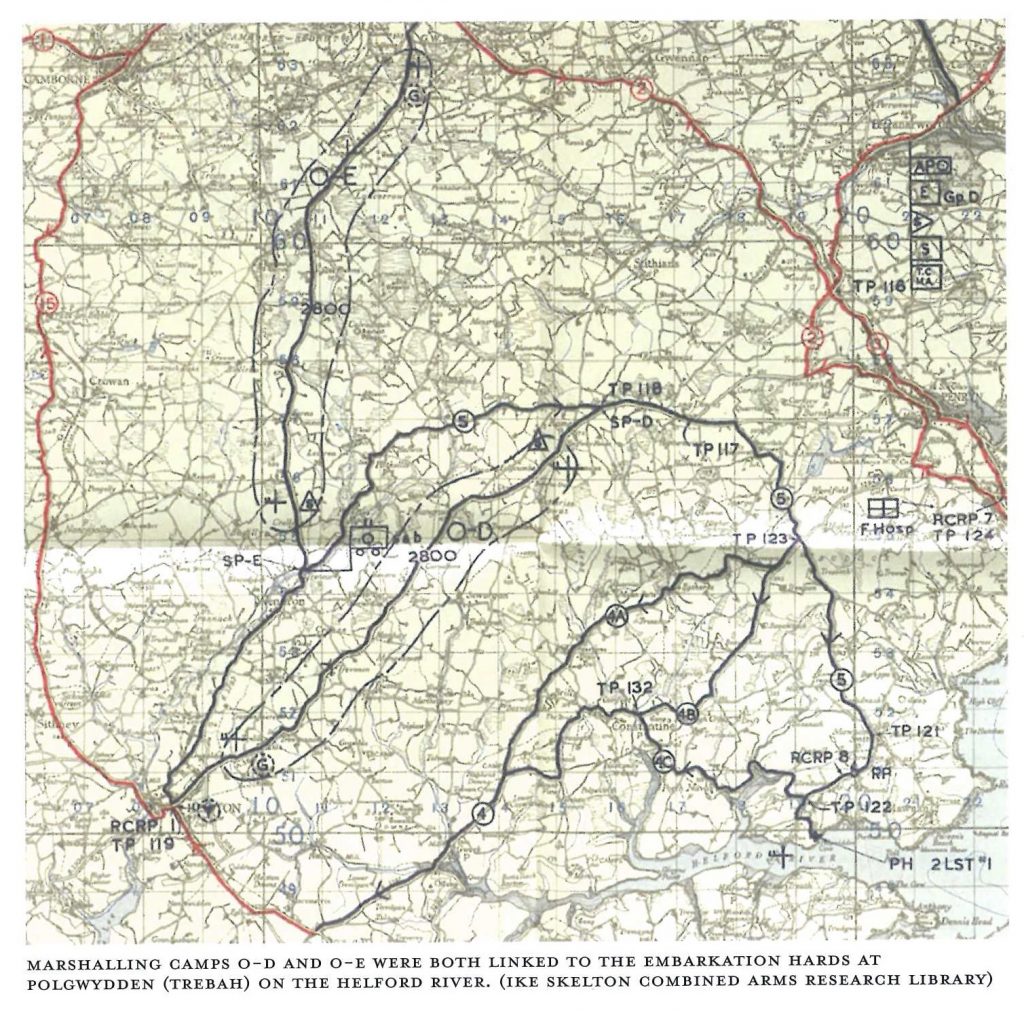
Image from ‘D-Day, Operation Overlord, Cornwall and Preparation for the D-Day landings
By Roderick De Normann
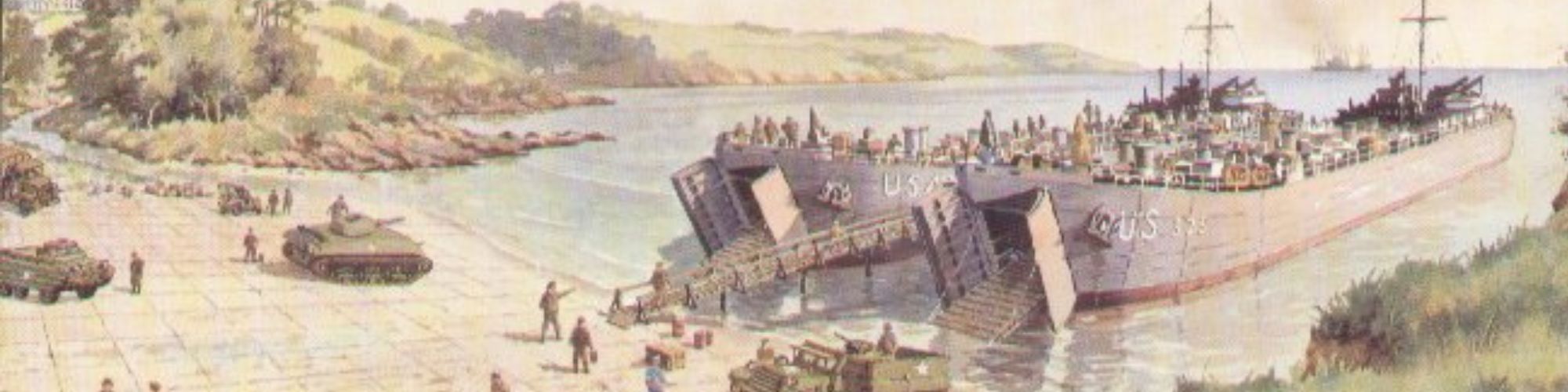
Landing craft tanks were designed to carry up to nine tanks or twelve lorries. These shallow draught vessels were designed with bows that opened to allow tanks and trucks to be driven straight on to the shore down a ramp.
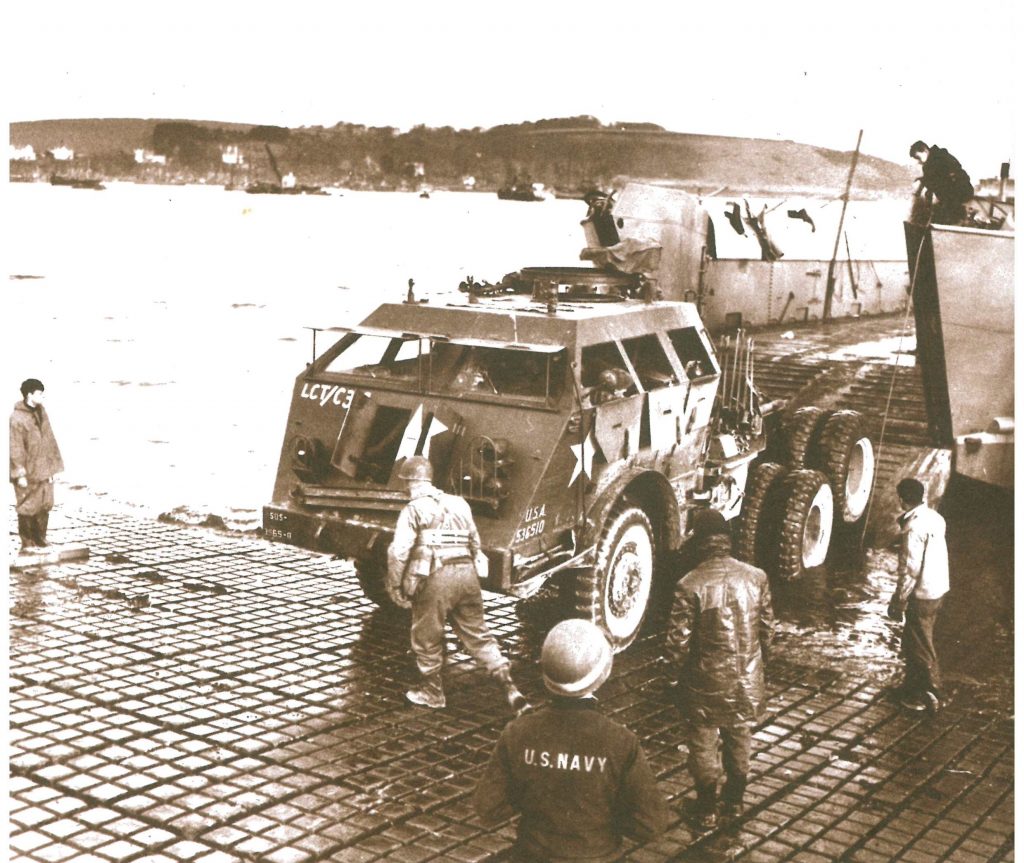

US Navy Tank Retriever loading an LCT at Grove Place, Falmouth, December 1943
(Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society)
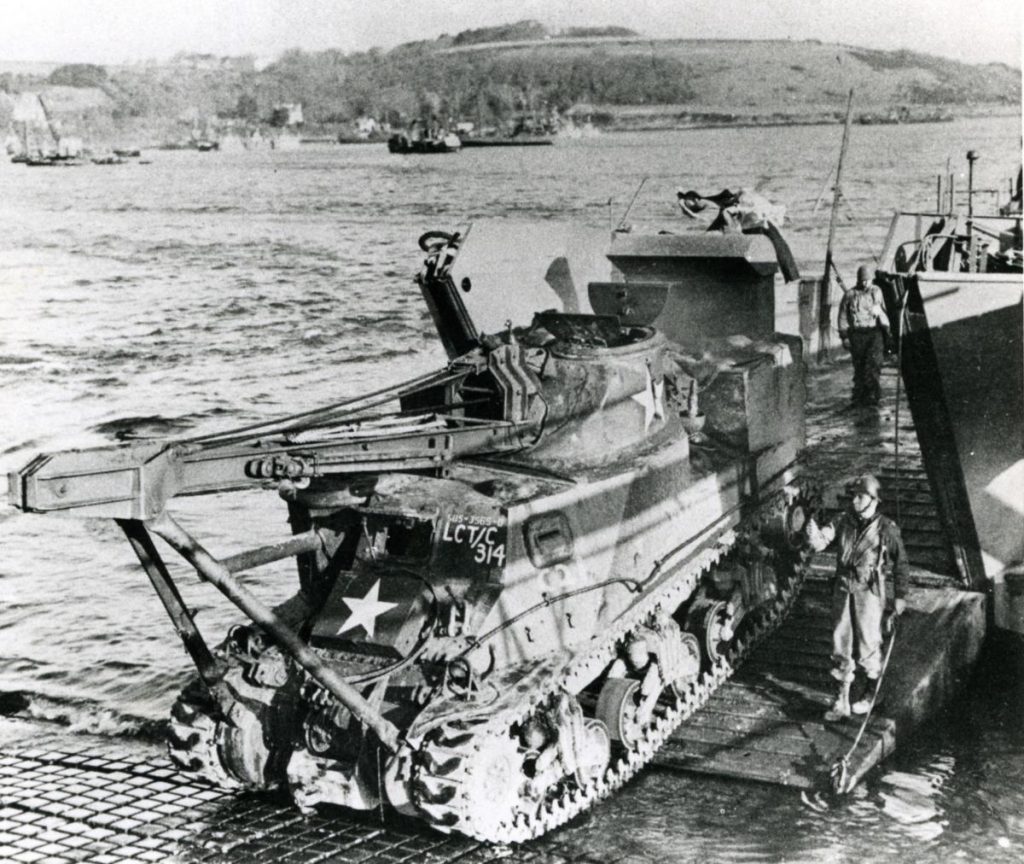
A tank landing craft embarks an Armoured Recovery Vehicle, an obsolete General Lee tank
fitted with a crane and powerful winches to recover disabled tanks on the battlefield
(Official US photograph in ‘Falmouth in Old Photographs’ by Peter Gilson)
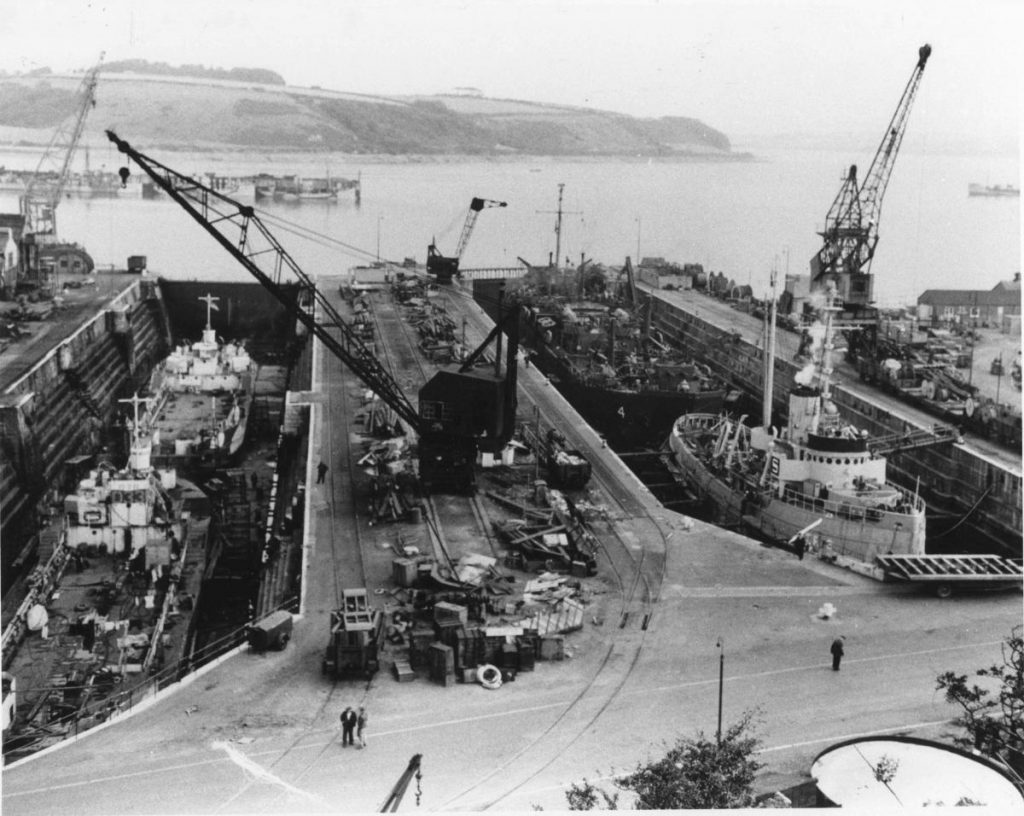

Invasion craft preparing for the D-Day landings at Falmouth Docks
(Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society)
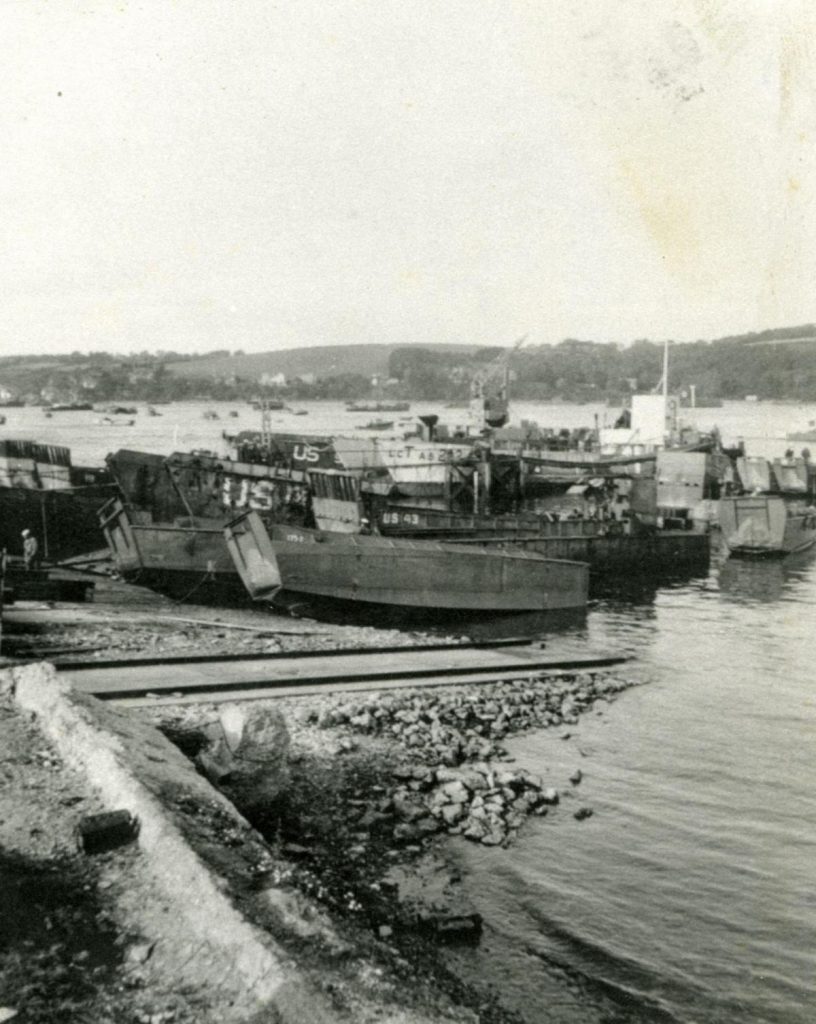

The hard at Grove Place Beach in Falmouth was used for the
smaller landing craft and assault ships of the US Navy
(‘The Lower Fal in Old Photographs’ by Peter Gilson)
Turnaware Point is on the Roseland side of the Fal river and was the site of one of the embarkation hards. The beach was levelled and laid with flexible concrete matting as early as 1943. Ammunition stores and Nissen huts were built amongst the trees in the woods to hide them from enemy observers.

Memorial at Turnaware
(Cornwall Heritage Trust website www.cornwallheritagetrust.org)
“To commemorate the D-Day Embarkation June 1944
from Turnaware Beach units of 29th Infantry Division, V. Corps, US Army
embarked for Normandy early June 1944 landing on
Omaha Beach the morning of D-Day, June 6th”.
“We will remember them”

This is all that remains of the two ‘Dolphin’ embarkation jetties from which the
29th Infantry Division, V Corps, US Army left for Omaha Beach in June 1944
(Wikimedia Commons image, Attribution Rabbi WP Thinrod,
Creative Commons Attribution – Share Alike 2.0 Generic license)
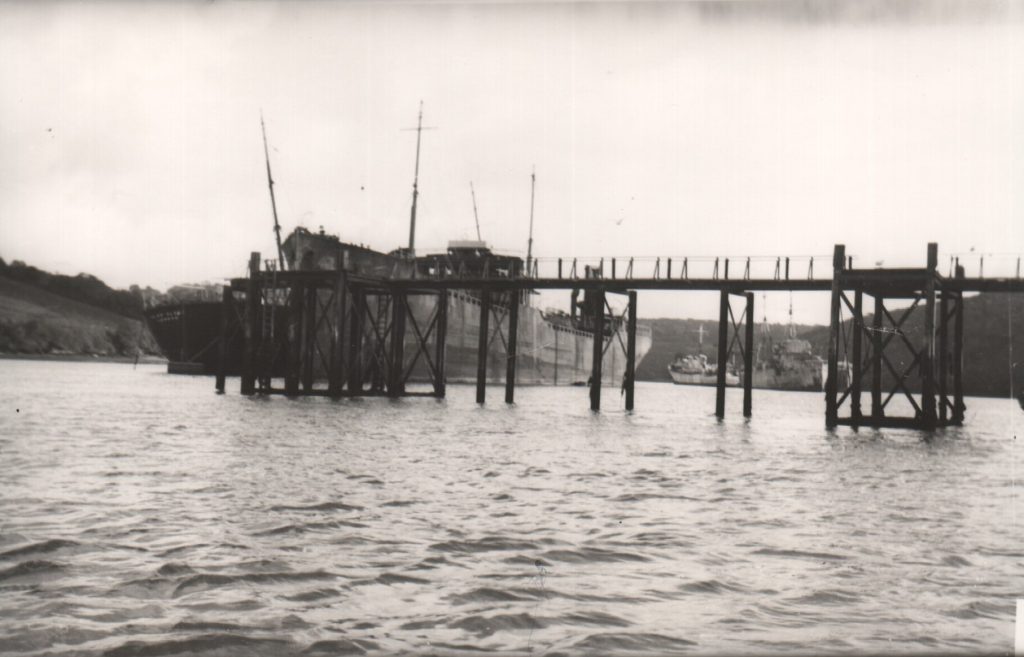

Dolphin Jetty built at Tolverne and used by the US Navy for servicing and loading landing craft.
(‘The Upper Fal in Old Photographs’ by Peter Gilson)
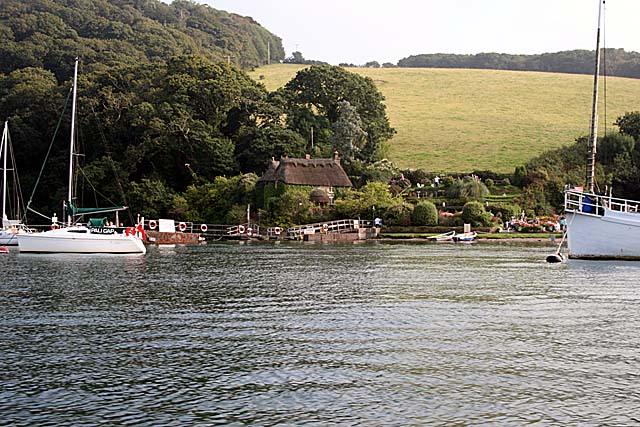

Smugglers Cottage at Tolverne
Wikimedia Commons image, Attribution Fred James,
Creative Commons Attribution – Share Alike 2.0 Generic license
Smugglers Cottage had been the home of the Newman family since 1934 and it was taken over by the Admiralty. The family continued to live in the rear of the building while the other rooms were used as offices and accommodation by US naval staff. It is recorded that General Eisenhower visited Smugglers Cottage when he inspected the troops in the area in 1944.

A memorial at Tolverne from the intoCornwall.com website
“This plaque commemorates the 50th anniversary of the departure of
thousands of American troops from this beach in landing craft bound for Omaha
on the Normandy coast for the invasion of Europe
D-Day June 6th 1944”
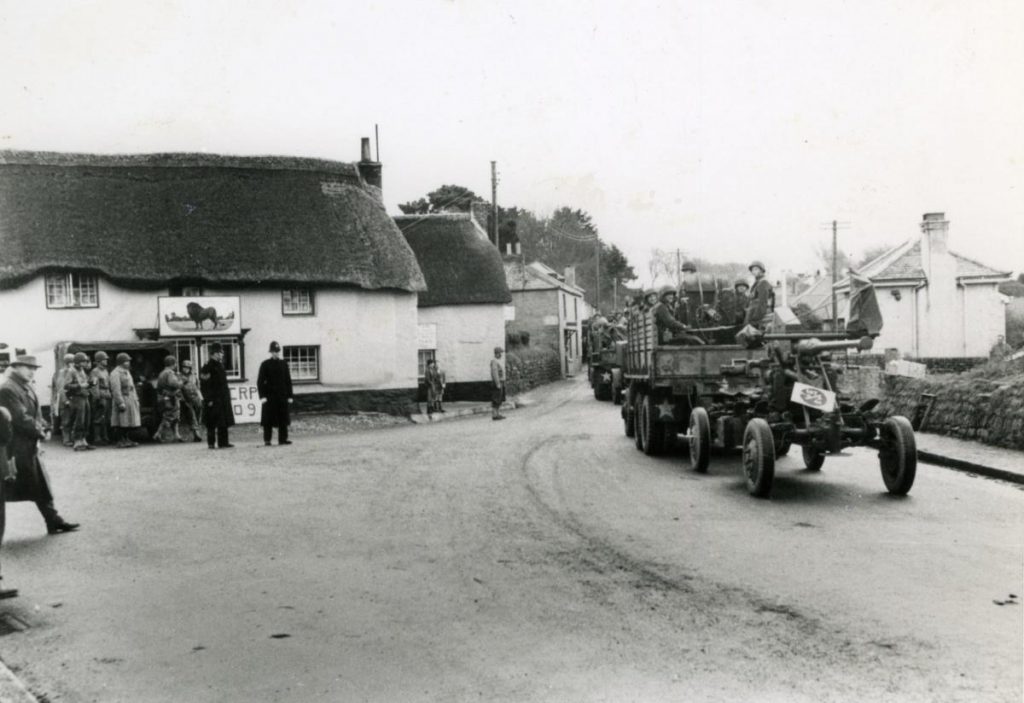

American troops driving through the village of Mawnan Smith to Polgwidden (Trebah Beach)
on the Helford ready for Operation Duck, one of the many rehearsals, passing the Red Lion pub.
(Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society).

A Trebah Gardens postcard of a similar image, colourised by Joshua Barrett from ‘Painting the Past’.

Display board on Trebah Beach
(Photograph by Lynne Vosper)
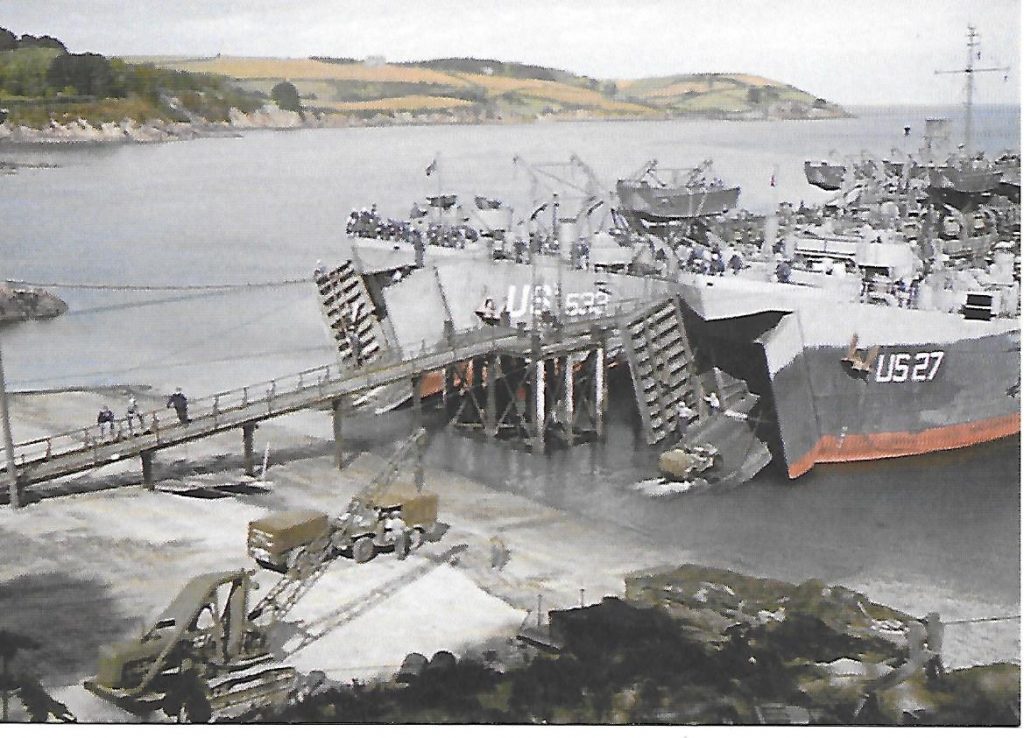

A Trebah Gardens postcard of a photograph showing loading of the LSTs,
colourised by Joshua Barrett from ‘Painting the Past’.
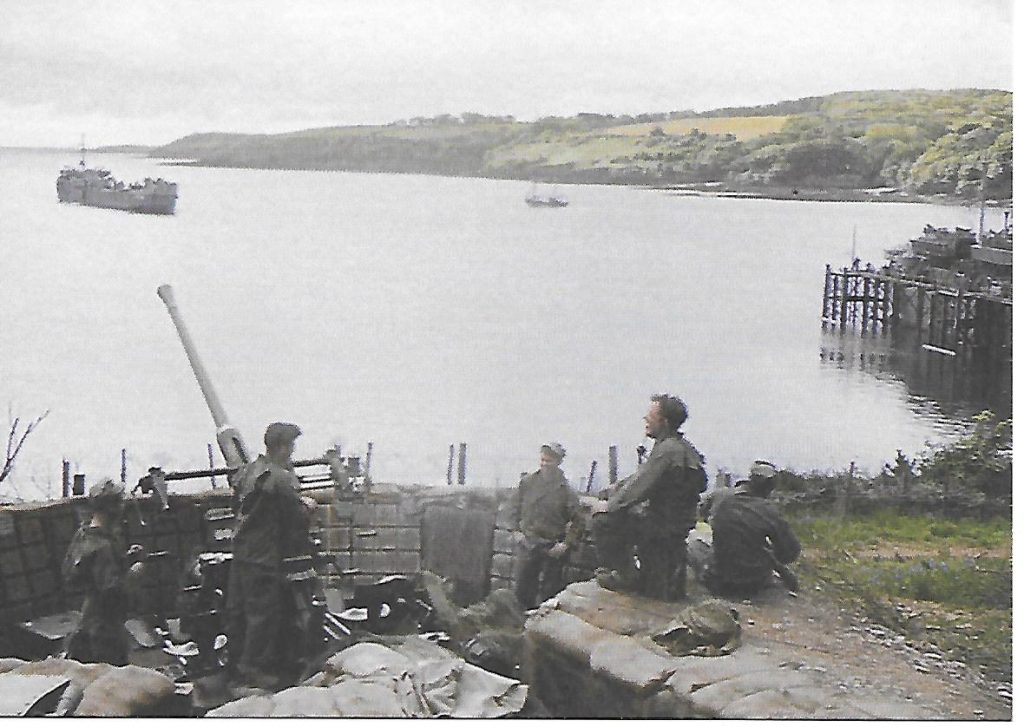

A Trebah Gardens postcard of a photograph of the armament at Trebah Beach,
colourised by Joshua Barrett from ‘Painting the Past’.

One of the two memorials at Trebah Beach.
(Photograph by Lynne Vosper)

Memorial at Trebah Beach
To the Officers and Men of the 29th Infantry Division
who embarked from Trebah in June 1944
for the D-Day assault on Omaha Beach, Normandy
We will remember them.
(Photograph by Lynne Vosper)
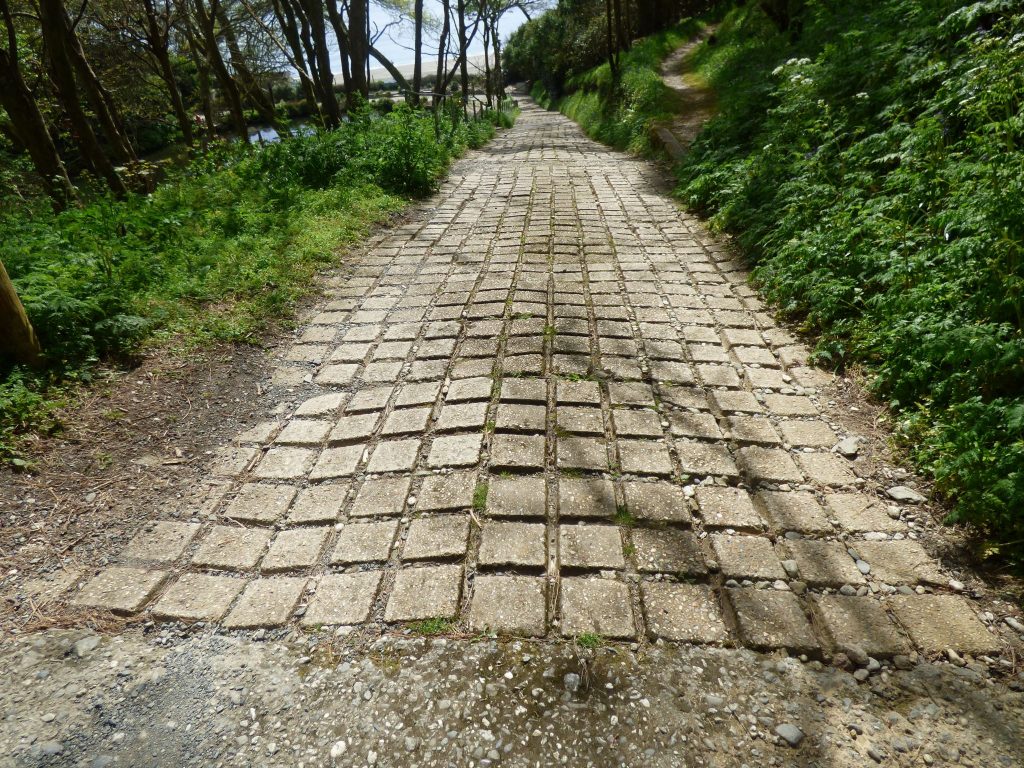

One of the footpaths leading down to the beach in Trebah Gardens was paved during
the 1960s using the concrete matting from the beach by Donald Healey of Austin Healey
car fame, one of the previous owners of the gardens.
(Photograph by Lynne Vosper)
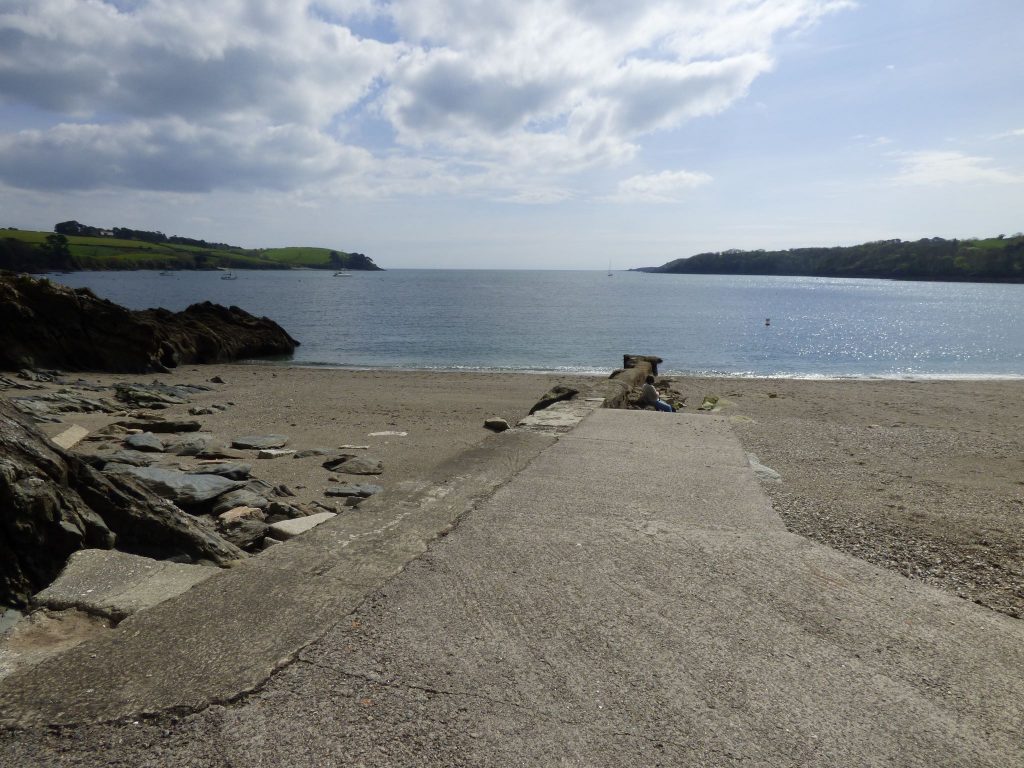

A tranquil scene at Trebah Beach
(Photograph by Lynne Vosper)
At the end of May 1944, the loading operations of military vehicles and equipment started at the embarkation points and the roads leading to Trebah, Turnaware, and Tolverne were filled with vehicles of all types. Moving the troops from their marshalling camps to the hards took several days. The Fal and Helford were full of LSTs waiting to load the troops, guns, ammunition and vehicles. From 1 June, the armada of LSTs left and suddenly all was quiet. They were gone. They joined other vessels from all along the south coast of England, battling through rough seas and gathering near the Isle of Wight before heading to Normandy. To convince the enemy that the main landing would be in Calais, elaborate plans were put in place with the aim of reducing German reinforcements on the Normandy coast.
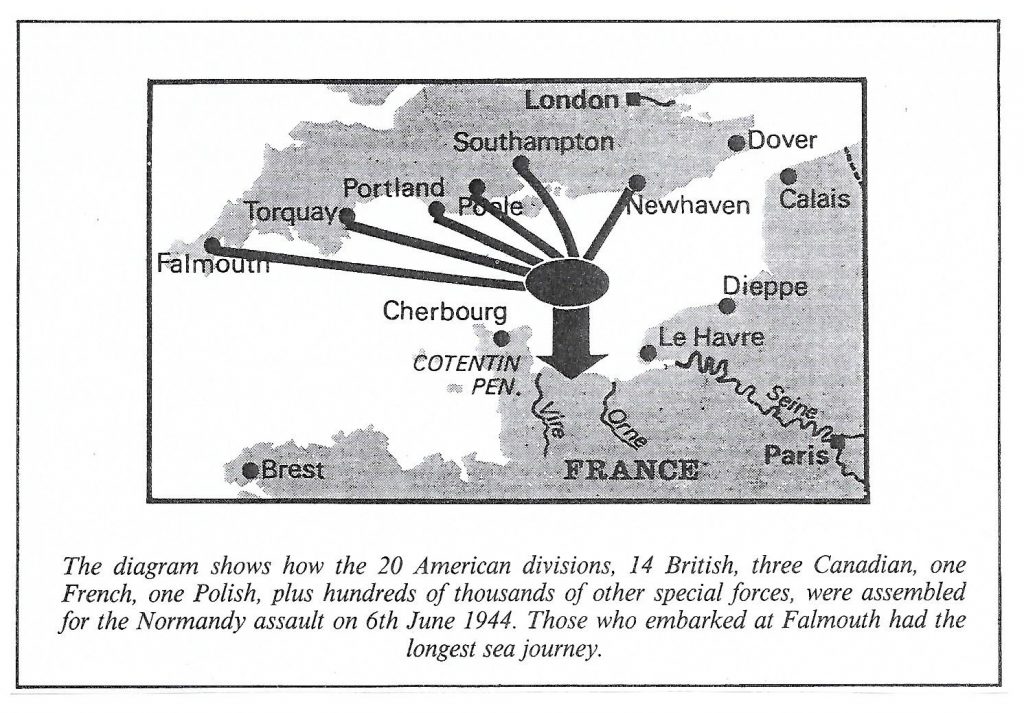
Diagram from ‘Falmouth at War’ by Bernard Breakell
In early June 1944, thousands of American troops left the beaches of Cornwall in landing craft bound for the Normandy coast of France to land on Omaha Beach as part of the invasion of Europe under General Dwight D Eisenhower, Supreme Commander of the Allied Forces, appointed by the President and Churchill. General Bernard Montgomery would head the land forces taking part, around 160,000 men. Most of the personnel that landed on the beaches of Normandy on D-Day were from the UK, the United States and Canada, and a significant number from Australia, Belgium, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, France, Greece, The Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, and Poland also took part in the Normandy Campaign.
The invasion was planned for 5 June but, due to adverse weather conditions, was delayed by 24 hours by General Eisenhower. Thankfully, a possible weather gap allowed Eisenhower to make his decision, D-Day would be on the 6 June 1944.

The weather report for 6 June 1944 reproduced by the
National Meteorological Library and Archive.
Copy held by the Bartlett Maritime Research Centre and Library
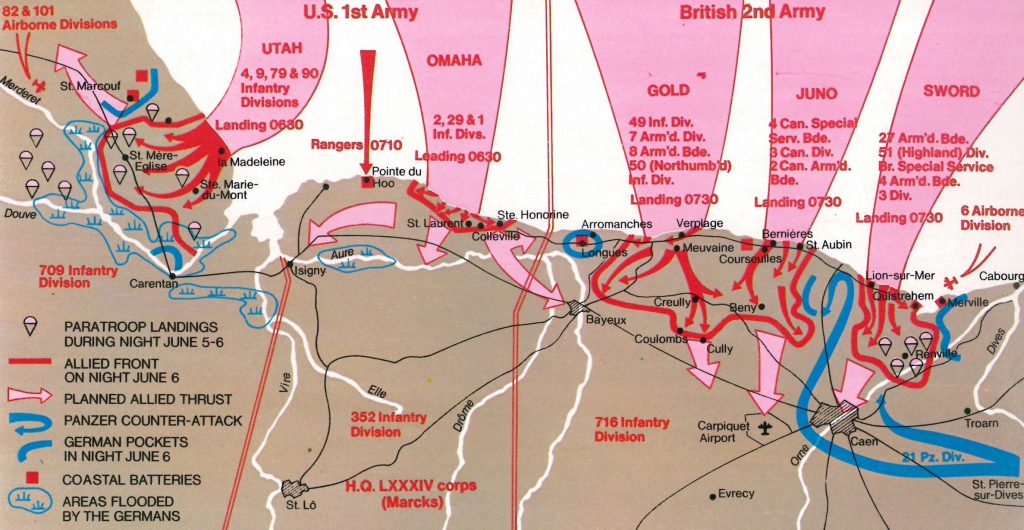
Image from World War II Magazine, No. 59, D-Day
Published by Orbis Publishing Limited.
The American troops who had been stationed in Cornwall from the 29th Infantry Division were destined for Omaha Beach. The casualties on Omaha Beach were the heaviest of any of the invasion beaches on D-Day with 2,400 casualties suffered by the US forces. This included wounded and killed as well as missing men.

Scroll presented to the US 29th Infantry Division on 31st May 2004 conferring
the Freedom of the Town of Falmouth
Source: The Commemorative Programme for Operation D-Day 60 in 2004.
The following books are available to view in the Bartlett Maritime Research Centre and Library.
Operation Cornwall 1940-1944 by Viv Acton and Derek Carter Cornish War and Peace by Viv Acton and Derek Carter Operation Overlord, Cornwall & Preparations for the D-Day Landings by Roderick de Normann. D-Day, Operation Overlord & Preparations for the D-Day Landings by Roderick de Normann. Falmouth at War by Bernard Breakell. Operation Neptune by Commander Kenneth Edwards, RN. Falmouth’s Wartime Memories as told to Trelawney. The Lower Fal in Old Photographs by Peter Gilson
There are also more photographs available on www.trebahgardens.co.uk
The Bartlett Blog is written and produced by the volunteers who staff The Bartlett Maritime Research Centre and Library of National Maritime Museum Cornwall. This blog post was written by Lynne Vosper, a Bartlett Library volunteer.
The Bartlett Maritime Research Centre & Library holds a Collection of over 20,000 volumes and offers access to one of the finest collections of maritime reference books, periodicals and archival material. The Bartlett Blog reflects the diversity of material available in The Bartlett Library.

National Maritime
Museum Cornwall Trust
Discovery Quay
Falmouth Cornwall
TR11 3QY
View Map
See our opening hours
Tel: +44(0)1326 313388
Email: enquiries@nmmc.co.uk